What is wire gauge?
Wire gauge is used as a standard method denoting wire diameter, measuring the diameter of the conductor (the bare wire) with the insulation removed. American Wire Gauge (AWG) is sometimes also known as Brown and Sharpe (B&S) Wire Gauge.
The higher the number - the thinner the wire. Typical household wiring is AWG number 12 or 14. Telephone wire is typical AWG 22, 24, or 26.
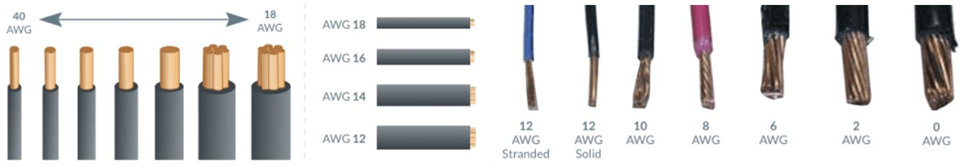
The AWG table is for a single, solid, round conductor. Because of the small gaps between the strands in a stranded wire, a stranded wire with the same current-carrying capacity and electrical resistance as a solid wire, always have a slightly larger overall diameter.
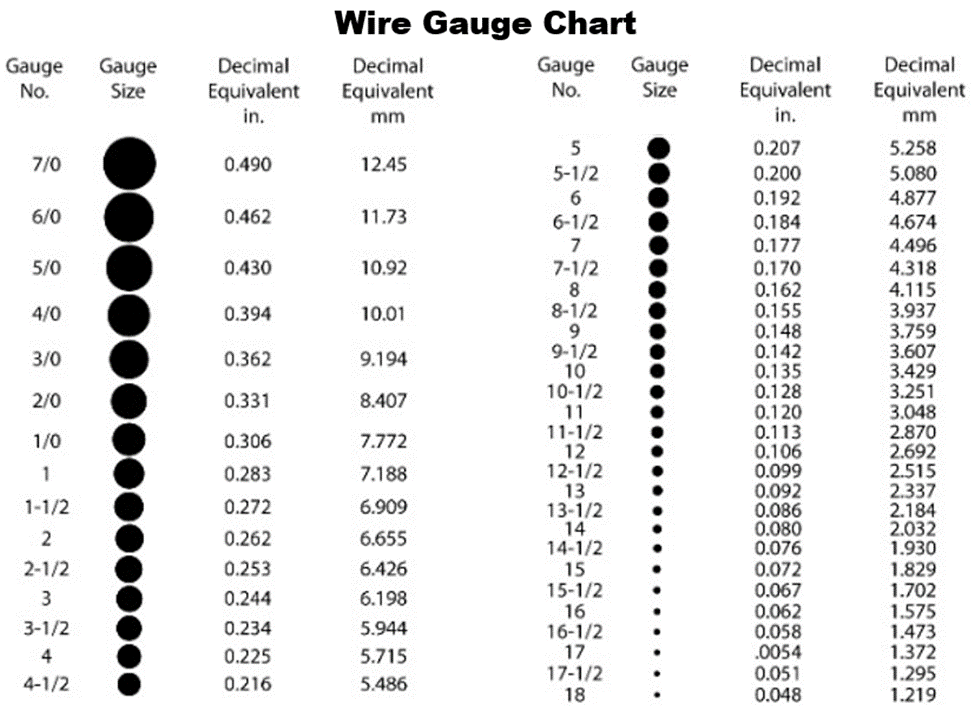
Verifying Wire Gauge
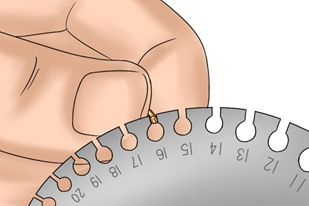
The gauge of wire can be checked by using a gauge plate. The parallel sided slots are used to make the measurement, whether you are measuring round wire or sheet metal. The enlarged hole at the bottom of the slot is there so that you can pass a wire through the gap into the enlarged space. The wire should exhibit a 'light dragging fit' in the slot itself and this drag should disappear as the wire enters the hole.
Current Ratings
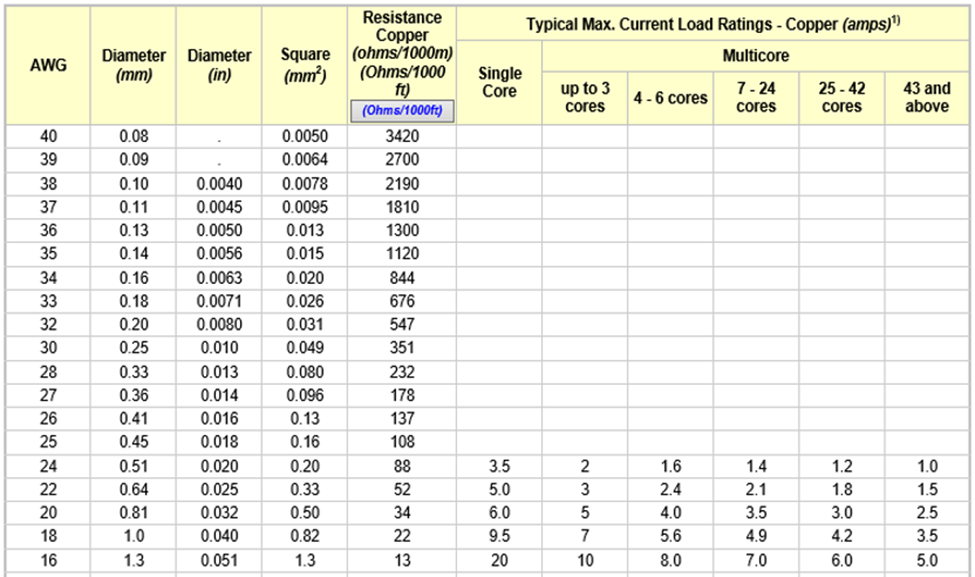
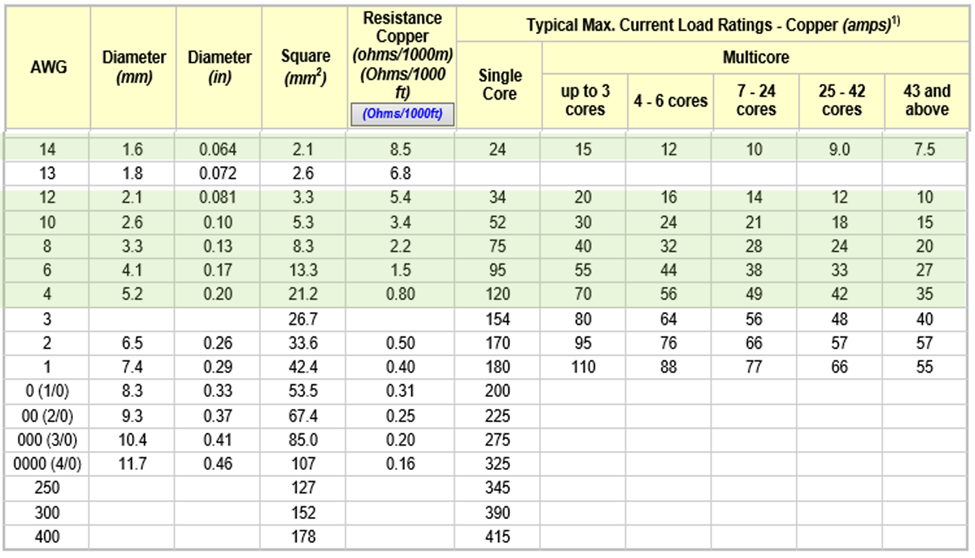
The table below indicates the current ratings of PVC-insulated single and multicore wiring cables. Be aware that the current load depends on installation method, the enclosure, and how well the resistance heat is removed from the cable. Operating temperature of the conductor, ambient temperature, and type of conductor insulation is important. Always check the manufacturer's data before detailed engineering.