How do I measure an O-ring?
How do I measure an O-ring?

There are several measuring devices available to determine the size of a replacement O-Ring.
If you do not have access to one of these tools. The instructions on how to measure them using a ruler or caliper are provided below.
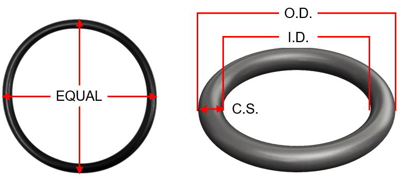 How to measure an O-ring:
How to measure an O-ring:
To measure an O-ring, you must measure the inside diameter (ID) or outside diameter (OD) and the width or cross (CS) of the O-ring.
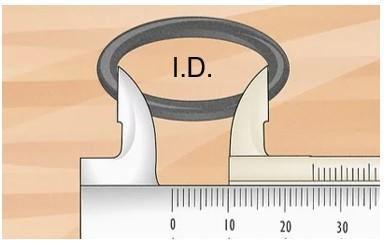
Step #1
Place the O-ring on a flat surface making sure it is round in shape (equal diameter in two directions at 90°). This is important to get an accurate measurement of the inside or outside diameter.
For the inside diameter, use a ruler or calipers to measure from one inner edge to the other at 180° through the center point. To calculate the inside diameter, ID= OD - (2 x CS).
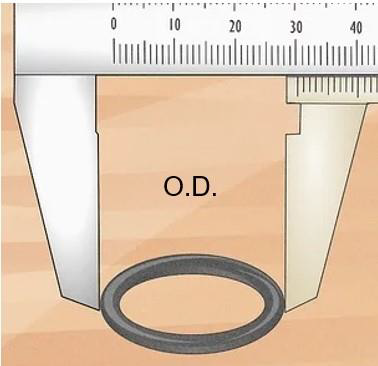
For the outside diameter, use a ruler or calipers to measure from one outer edge of the O-ring to the other outer edge at 180° through the center point. To calculate the outside diameter, OD = ID + (2 x CS).
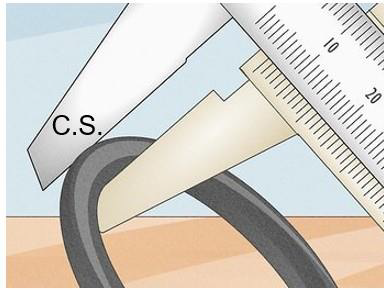
Step #2
To measure the cross section, place the O-ring into a vernier caliper. Lightly clamp the jaws of the caliper onto the O-ring, but do not compress it. Record the thickness of the ring, this is the cross section. To calculate the cross section, CS = (OD - ID) ÷ 2.
If the O-ring is cut, measure the cross section and the length. To calculate the inside diameter from the length, ID= (Length ÷ 3.142) - CS.
With the above dimensions you can determine the proper O-ring size. A proper fit is critical when replacing an O-ring. There are two main O-ring sizing types, “standard” and “metric.” Standard was developed for use in the United States, while the international community uses metric sizes.
Standard Sizes (AS568B):
The standard sizes used by O-ring manufacturers in the United States are defined by Aerospace Standard AS568B, Aerospace Size Standard for O-rings. That document, published by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), lists the sizes of O-rings. Cross-sectional diameters range from 0.040 to 0.275 inches. Inside diameters range from 0.029 to 25.940 inches. There are 369 standard sizes.
Metric Sizes:
Metric sizes for O-rings are defined by International Standard ISO 3601-1:2002: Fluid power systems O-rings, Part 1: Inside diameters, cross-sections, tolerances, and size identification code. That standard groups metric sizes into two series, G and A. The G series is used for general purpose applications and includes a wide range of inside diameters. The A series is used for aerospace applications where tighter tolerances are recommended. The G series has 445 sizes and the A series has 383 sizes.
ISO cross-sectional diameters differ from the Aerospace Standard by less than 0.001 inch. Therefore, many AS568B sizes are interchangeable with an ISO size. Be sure to consult ISO 3601-1 for specific dimensions, as inside diameters may differ.
Additional Resources:
https://support.boshart.com/do-you-have-dimensions-for-standard-as568-o-rings
https://support.boshart.com/what-should-i-use-to-lubricate-o-rings
