Bottle type shallow well air volume control (air charger) operation.
Bottle type shallow well air volume control (air charger) operation.
Your pressure system may have either of two basic types of pressure tanks which are "Hydro Pneumatic Tanks" a.k.a. Atmospheric Tanks and "Captive Air” Tanks” a.k.a. Pre-Charged, Diaphragm or Bladder Tanks.
Shallow Well Jet Pump AVC (a.k.a. AIR CHARGERS)
In shallow well pump installations, in which the jet pump is at the surface and creates a vacuum which draws water from the well (more accurately allows the atmospheric pressure in the well to push the water to the surface) typically these will not pump water from any deeper than approx. 28 ft. and the higher the elevation is from sea level the pumping depth with decrease accordingly.
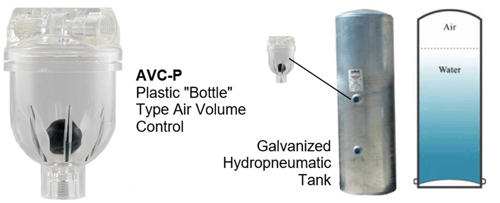
Hydro Pneumatic type tanks use the air within the tank to maintain pressure on the water system. Air unlike water, air can be compressed, and this compressed air acts like a giant spring which pushes the water from the tank providing water between the pump cycles (drawdown). Over time, the captive air can be absorbed into the water, reducing the internal tank pressure and useable water between pump cycles, this will eventually result in a waterlogged tank. The remedy is to drain the tank, so the air is replaced or to pump air into the system thru an air valve.
AVC-P INSTALLATION
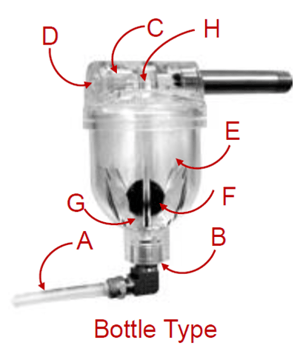
The Bottle Type Air Volume Control is mounted in the tank accessory port about 1/2 way up the tank. A 1/4" tubing (A) is connected from the Air Volume Controls lower ¼: FPT connection to the suction side of the pump.
 BOTTLE TYPE AIR CHARGERS (AVC) OPERATION
BOTTLE TYPE AIR CHARGERS (AVC) OPERATION
When the pump starts, air is drawing thru the check valve (C) and inlet port (D) until the bottle chamber (E) is full of air at which time the floating ball (F) closes against the lower valve seat (G) and no more air is drawn in thru the remainder of the pumping cycle.
When the pump stops the air that is trapped in the chamber (E) bubbles up thru the ball check valve (H) thru the tank connection of the AVC (I) into the tank thru the short pipe nipple. The floating ball (F) rises to the top of the air chamber and the air charger is rest for the next pump cycle.
