Are your 00806 Series Brass Swing Check Valves suitable for Oil and Gas Applications?
Are your 00806 Series Brass Swing Check Valves suitable for Oil and Gas Applications?
The simple answer is YES! However, they are not suitable for combustible gases! We must cover the “G” for gas in the W.O.G. valve rating in more detail.
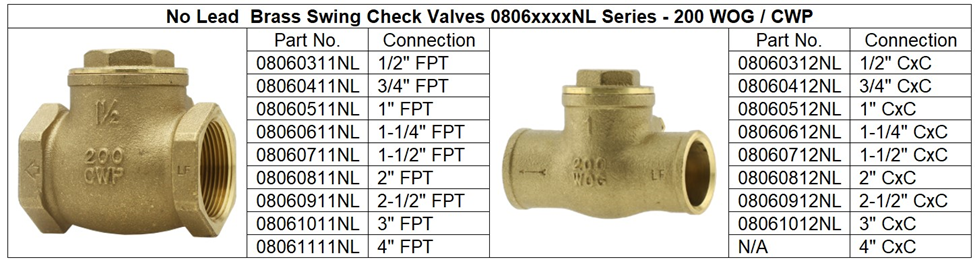
Let us start with, what does W.O.G. Stand for?
WOG stands for Water-Oil-Gas and is used to indicate the pressure rating of valves and fittings
“WOG” - General “Non-Shock” pressure rating indicating maximum P.S.I. for the medias Water, Oil or Gaseous. It has traditionally been used as a catch all for ambient temperature fluids, simply defined as water, oil or gas.
W - WATER
“W” The definition of WATER is clear – H²O.
The terms oil and gas are less clear and are the cause of major confusion!
O - OIL
“O” We think of OIL as a hydrocarbon (a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon). The majority of hydrocarbons found naturally occur in crude oil, where decomposed organic matter provides an abundance of carbon and hydrogen. However, oils are also made from animal fats and vegetables. In valve selection, oil is a liquid that is thicker than water, has lubricating characteristics and flows freely.
G - GAS
“G” GAS is meant as a vaporized liquid. Gas then can be air, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, etc.
WARNING: WOG does NOT cover combustible gases!
Valves for natural gas and liquid propane for example must have the required gas approvals from CSA – always make sure to verify and follow the installation codes for your area! W.O.G. Rating Does not cover FLAMABLE Gases Natural Gas (NP) or Liquid Propane(LP)
NOTE:
The WOG rating has not been a good description and there is movement within the industry to the more descriptive CWP (Cold Working Pressure) Rating
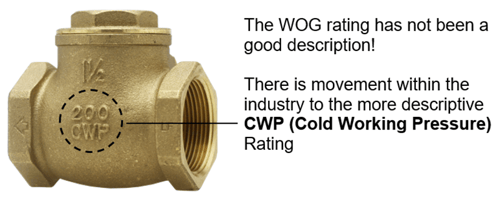
Regardless of what it is called, it remains a limitation of the pressure valve only. The valve type, material and trim are different for each application. The pressure / temperature limitations of the pressure containing vessel are a few of the several variables that must be considered.

