What are RoHS and REACH?
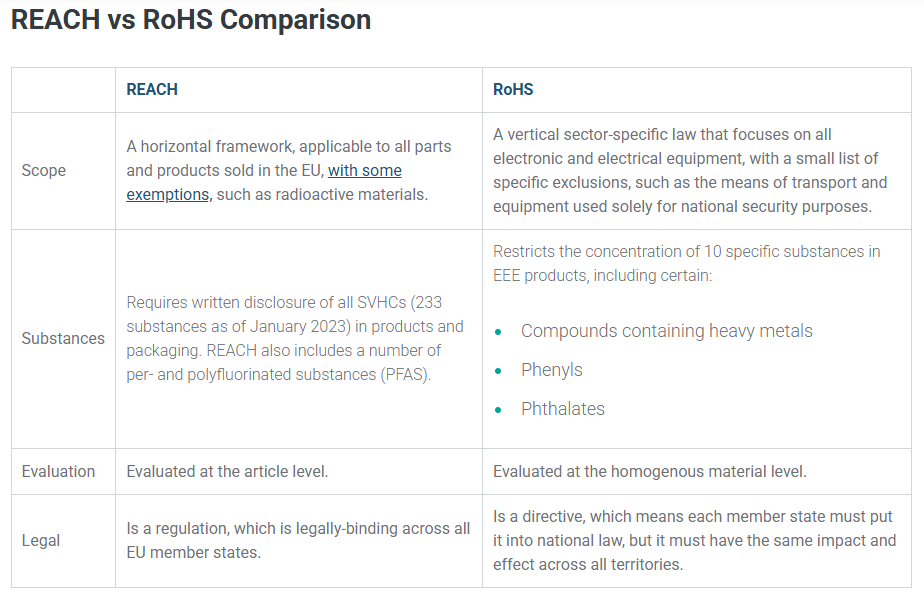
The European Union (EU) Registration, Evaluation, Authorization, and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) Regulation and the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) Directive have many things in common. They restrict the use of potentially dangerous substances in all products sold. Both the EU REACH Regulation and the EU RoHS Directive aim to reduce and restrict substances that can be deemed harmful to humans and the environment.
There is some overlap between the legislations. When a substance is already covered under the RoHS Directive is added to the REACH SVHC Candidate List, enforcement authorities make an effort to ensure there is no conflict between requirements and that controls are consistent. There is a common understanding that RoHS should be given priority to regulate all issues pertaining to the use of substances in Electrical and Electronic Equipment (EEE).
One more thing both REACH and RoHS have in common is the risk associated with non-compliance. Non-compliance with either lae can result in reputation damage, loss of market access, recall of goods, loss of revenues, and/or fines.
What is RoHS Compliance?
The RoHS Directive seeks to limit the impact and exposure of specific hazardous substances to consumers and the environment, and reduce occupational exposure when products or equipment are manufactured, recycled, or sent for final disposal. Electrical and electronic products, and all accessories sold with them, cannot be placed on the market if they contains RoHS restricted substances above maximum concentration limits. RoHS does include exemptions that allow some restricted substances to be used in certain very technical and specific applications if a suitable substance is not available on the market or that substitute has a greater environmental impact.
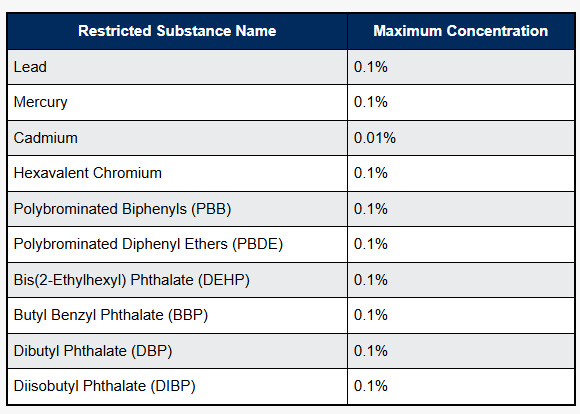
It currently restricts the use of ten substances: lead, mercury, cadmium, hexavalent chromium, polybrominated biphenyls (PBB), and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDE), bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP), butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP), dibutyl phthalate (DBP) and diisobutyl phthalate (DIBP). All products with an electrical and electronic component, unless specifically excluded, have to comply with these restrictions.
What is REACH Compliance?
To achieve REACH Compliance, companies must have an ongoing product compliance program that shows continuous improvement. This includes collecting and maintaining chemical information and documentation from suppliers.
REACH focuses on substances of very high concern (SVHCs) on the Candidate List, substances that require authorization (Annex XIV), and restricted substances (Annex XVII). These lists are managed by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) on behalf of EU member states and the European Commission.
Companies must review their products and components to ensure restricted substances are not used, or that they meet all applicable restrictions. If a substance is listed under Annex XIV, companies must obtain authorization before using it in the EU.
